
A Desktop Environment (DE) is a graphical user interface (GUI) that provides a cohesive and intuitive user experience for managing files, running applications, and customizing system settings on a computer. DEs include various components, such as window managers, panels, file managers, desktop icons and application launchers, all integrated into a unified interface.
Desktop Environments play a crucial role in modern operating systems, Linux included. They are purpose-built to enhance user experience and simplify the management of the system, without requiring users to possess advanced command-line interface knowledge.
Importance of choosing the right Desktop Environment
Choosing the right Desktop Environment is an important decision for Linux users. A DE affects how users interact with their computer and can significantly impact their productivity, workflow, and user experience. For example, a user who prefers a simple and lightweight interface may prefer a minimalistic DE like Xfce, while a user who prioritizes customization and eye-candy may prefer a feature-rich DE like KDE.
It is also important to consider the hardware resources of a computer while choosing a DE. Resource-intensive DEs like GNOME and KDE require more processing power and memory, while lightweight DEs like Xfce can run on older or low-end hardware.
Overview of GNOME, KDE and Xfce
There are many Desktop Environments available for Linux but GNOME, KDE and Xfce are the most popular and widely used.
GNOME is a popular DE for Linux that emphasizes simplicity and modern design. It features a clean and intuitive interface with a focus on productivity and ease of use. GNOME is widely used on many popular Linux distributions like Fedora, Ubuntu and Debian.
KDE is another popular DE that offers a highly customizable and feature-rich interface. It features a modern and sleek design with a wide range of customization options, including widget support and extensive theming capabilities. KDE is used on popular distributions like OpenSUSE, Kubuntu and Manjaro.
Xfce is an adaptable and speedy Desktop Environment, characterized by its lightweight design and extensive customization options. It prioritizes utility and efficiency over embellishments, with a minimalistic interface that is both user-friendly and straightforward. As a result of its efficiency, Xfce is a popular choice for lightweight Linux distributions, such as Xubuntu, Manjaro Xfce and MX Linux.
In summary, GNOME, KDE and Xfce are three of the most popular Desktop Environments for Linux. Each has its own unique features, design philosophies, and resource requirements. Choosing the right DE is an important decision that depends on a user’s hardware resources, preferences and workflow.
GNOME Desktop Environment

Introduction to GNOME
GNOME, a well-known Linux Desktop Environment, prioritizes modern design, productivity and simplicity. It caters to Linux beginners by being user-friendly and accessible. The GNOME Foundation, a non-profit organization committed to producing a free and open computing platform, drives the development of GNOME. The project is also open-source, allowing for community contributions.
GNOME Features and Usability
GNOME prides itself on having a user-friendly and productive interface, which is intuitive and easy to navigate. Its minimalist design and simplified workflow aim to provide users with a smooth and efficient experience. GNOME boasts several features, including:
- Activities Overview: A central hub for managing applications, windows and workspaces.
- Nautilus File Manager: A powerful and intuitive file manager with support for previews, bookmarks and integrated search.
- GNOME Shell: A customizable and lightweight window manager that provides a modern and elegant interface.
- GNOME Terminal: A powerful terminal emulator that allows users to access the command-line interface.
- GNOME Settings: A unified and intuitive settings panel for configuring system settings and preferences.
Pros and Cons of GNOME
Like any Desktop Environment, GNOME has its pros and cons.
Pros:
- User-friendly: GNOME is designed to be accessible and user-friendly, making it an excellent choice for new Linux users.
- Modern Design: GNOME’s sleek and modern design provides a clean and minimalist interface that emphasizes productivity.
- Integration with Linux ecosystem: GNOME is integrated with many Linux distributions and provides seamless access to popular Linux applications.
- Active development: GNOME is an open-source project with an active development community, ensuring that it receives regular updates and improvements.
Cons:
- Resource-intensive: GNOME can be resource-intensive and may not perform well on older or low-end hardware.
- Limited customization: GNOME’s design philosophy emphasizes simplicity, which can limit the customization options available to users.
- Some features may be hidden: Some advanced features may be hidden, making it difficult for users to access them.
Popular Distributions that use GNOME
GNOME is used as the default Desktop Environment on many popular Linux distributions, including:
Fedora: Fedora is a popular Linux distribution that uses GNOME as its default Desktop Environment.

Ubuntu: Ubuntu is another popular distribution that offers a GNOME-based version called Ubuntu GNOME.
Debian: Debian offers a GNOME-based version called Debian GNOME, which provides a stable and reliable desktop environment.
Arch Linux: Arch Linux provides a GNOME-based version called Arch GNOME, which offers a minimalistic and customizable interface.
GNOME is a widely used Linux Desktop Environment that boasts a modern and user-friendly interface. It comes pre-installed or readily available in many Linux distributions, offering easy access to popular Linux applications. Although it may be resource-intensive and have limited customization options, it remains an excellent choice for beginners to Linux and those who prioritize productivity and simplicity.
KDE Desktop Environment

Introduction to KDE
KDE is another popular Desktop Environment for Linux that provides a powerful and customizable interface. Users will have the most freedom and control possible over their computing experience thanks to its design. The KDE community, a collection of volunteers committed to building a free and open computing platform, drives the development of KDE, an open-source project.
KDE Features and Usability
KDE offers a robust and adaptable user interface that prioritises efficiency and usability. Some of its characteristics are:
- Plasma Desktop: A customizable and feature-rich desktop environment that provides an intuitive interface.
- Dolphin File Manager: A powerful and intuitive file manager with support for previews, bookmarks and integrated search.
- Konsole Terminal: A powerful terminal emulator that allows users to access the command line interface.
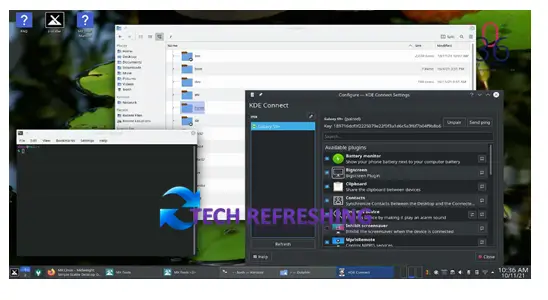
- KDE Connect: A feature that allows users to connect their Android phone to their KDE desktop and provides features such as notifications, file sharing and remote input.
- KDE Applications: A suite of applications that are designed to work seamlessly with the KDE environment, including a web browser, office suite and media player.
Pros and Cons of KDE
Like any Desktop Environment, KDE has its pros and cons.
Pros:
- Customizable: KDE provides a high degree of customization, allowing users to configure the interface to their liking.
- Feature-rich: KDE provides a rich set of features that can increase productivity and improve the user experience.
- Integration with Linux ecosystem: KDE is integrated with many Linux distributions and provides seamless access to popular Linux applications.
- Active development: KDE is an open-source project with an active development community, ensuring that it receives regular updates and improvements.
Cons:
- Resource-intensive: KDE can be resource-intensive and may not perform well on older or low end hardware.
- Steep learning curve: KDE’s high degree of customization can be overwhelming for new Linux users.
- Inconsistent design: KDE’s design can be inconsistent and may not appeal to everyone.
Popular Distributions that use KDE
KDE serves as the default Desktop Environment on numerous well-known Linux distributions, such as:
Kubuntu: Kubuntu is a popular Linux distribution that uses KDE as its default Desktop Environment.

openSUSE: openSUSE offers a KDE-based version called openSUSE KDE, which provides a stable and reliable desktop environment.

Mageia: Mageia provides a KDE-based version called Mageia KDE, which offers a user-friendly and customizable interface.

Neon: Neon is a KDE-based Linux distribution that provides the latest stable release of KDE.
KDE is a feature-rich and highly customizable Desktop Environment for Linux that integrates well with commonly used Linux applications. Though it may consume significant resources and require a considerable learning curve, it proves to be an ideal option for proficient Linux users who prioritize controlling and customizing their computing experience.
Xfce Desktop Environment

Introduction to Xfce
Xfce is an open-source and lightweight Desktop Environment for Linux, which prioritizes ease of use and customization. It is noted for its quick and effective performance and is maintained by a group of volunteers. Those that seek a quick and light desktop environment will find Xfce to be the ideal choice because it strives to create a balance between simplicity and capability.
Xfce Features and Usability
Easy usage and performance are prioritised in the straightforward, adaptable interface that Xfce offers. Among its characteristics were:
- Xfce Panel: A customizable panel that provides access to frequently used applications and system settings.
- Thunar File Manager: A fast and lightweight file manager that supports advanced features like bulk renaming, split-view mode and tabbed browsing.
- Xfce Terminal: A simple and fast terminal emulator that provides access to the command line interface.
- Xfce Settings Manager: A central location to customize Xfce settings, including the desktop appearance, window manager and keyboard shortcuts.
- Xfce App Finder: A simple and efficient application launcher that makes it easy to find and launch applications.
Pros and Cons of Xfce
Like any Desktop Environment, Xfce has its pros and cons.
Pros:
- Lightweight: Xfce is a lightweight Desktop Environment that can run on older or low-end hardware.
- Fast: Xfce is fast and responsive, making it an excellent choice for users who value performance.
- Simple: Xfce provides a simple and easy-to-use interface that is accessible to all users.
- Customizable: Xfce provides a high degree of customization, allowing users to configure the interface to their liking.
Cons:
- Limited features: Xfce’s focus on simplicity means that it may lack some of the advanced features provided by other Desktop Environments.
- Inconsistent design: Xfce’s design can be inconsistent and may not appeal to everyone.
- Limited support: Xfce is maintained by a small community of volunteers, which may limit its support and development.
Popular Distributions that use Xfce
Xfce serves as the default Desktop Environment on numerous well-known Linux distributions, such as:
Xubuntu: Xubuntu is a popular Linux distribution that uses Xfce as its default Desktop Environment.

Manjaro: Manjaro provides a version called Xfce Edition, which provides a lightweight and easy-to-use interface.

MX Linux: MX Linux is a popular Linux distribution that uses Xfce as its default Desktop Environment and emphasizes performance and usability.
Fedora Xfce Spin: Fedora provides a version called Xfce Spin, which provides a lightweight and customizable interface.
Xfce is a lightweight, quick Desktop Environment for Linux that offers a user-friendly interface. For users who value performance, simplicity and customisation, it is a great option even though it may lack some of the more sophisticated capabilities offered by other Desktop Environments.
Comparison of GNOME, KDE and Xfce
Resource Usage
Resource usage is an important consideration when choosing a Desktop Environment, especially if you are using older or low-end hardware. Xfce is the lightest of the three, but GNOME is reputed to be the heaviest. KDE occupies a middle ground. While Xfce is made to run on older technology with constrained resources, GNOME requires more resources to function smoothly.
Customizability
When selecting a Desktop Environment, customization is a crucial consideration. KDE stands out as the most customizable among the three, boasting an extensive selection of options for customizing themes, widgets and plugins. GNOME also offers a significant level of customization, though not to the same extent as KDE. While Xfce is the least customizable of the three, it still offers a respectable range of customization options.
User Interface and Design
User interface and design are subjective factors since various users may have varied preferences for design aesthetics. GNOME offers a sleek, contemporary user interface that puts an emphasis on usability and simplicity. KDE offers a more conventional user interface with an emphasis on usefulness and customization. With an emphasis on usability and performance, Xfce offers a straightforward and easy-to-use interface.
Compatibility and Availability of Applications
Compatibility and application availability are also crucial factors to consider when selecting a Desktop Environment. With a large user base, both GNOME and KDE have numerous applications developed specifically for their respective environments. On the other hand, Xfce may have a smaller user base, resulting in fewer applications developed explicitly for this environment. Nonetheless, all three environments can run the same applications, provided they are compatible with the underlying Linux distribution.
Performance and Speed
For users who prioritize performance over aesthetics, speed and performance are crucial factors to consider. Among the three environments, Xfce is recognized as the swiftest and most lightweight, making it a great option for older or low-end hardware. KDE is slightly slower than Xfce but still delivers good performance. In contrast, GNOME is the slowest of the three, yet it is still speedy enough to run without issues on most contemporary hardware.
All three Desktop Environments have their pros and cons. GNOME provides a modern and clean interface, KDE provides a high degree of customization and Xfce provides a lightweight and fast interface. When choosing a Desktop Environment, it is important to consider your hardware specifications, personal preferences and the applications you intend to use.
Choosing the Right Desktop Environment
Understanding your System Requirements
To make an informed decision about the best Desktop Environment for your system, it is essential to consider your hardware specifications. Various Desktop Environments have varying resource requirements, and some may not perform efficiently on older or low-end hardware. For instance, if your system has limited RAM and processing power, it may be preferable to choose a lightweight Desktop Environment such as Xfce. Conversely, if you have a contemporary system with ample resources, you may opt for a more feature-rich environment such as KDE or GNOME.
Considering your User Needs and Preferences
When choosing a Desktop Environment, it is crucial to take into account your user preferences and needs. Users have varying preferences concerning design, customization and functionality. For instance, if you favor a modern and sleek interface, GNOME may be the ideal choice. If you prefer a traditional interface with extensive customization options, KDE may be more suitable. On the other hand, if you prioritize speed and performance, Xfce may be the optimal option.
Popular Linux Distributions and their Default Desktop Environments
Numerous prevalent Linux distributions come with a preselected Desktop Environment, typically selected according to the distribution’s intended audience and objective. For instance, Ubuntu utilizes GNOME as its default Desktop Environment, while Linux Mint uses Cinnamon, which is founded on GNOME. Fedora employs GNOME as its default, while openSUSE uses KDE. Xubuntu, a variation of Ubuntu designed for older hardware, employs Xfce as its default. It’s essential to remember that you can always modify the default Desktop Environment or install multiple environments and alternate between them.
Selecting the appropriate Desktop Environment depends on several factors, such as your system requirements, user needs and personal preferences. Being aware of these factors can assist you in making an informed decision and finding a Desktop Environment that is most suitable for you. Additionally, it’s vital to remember that you can always alter your Desktop Environment later, so don’t hesitate to experiment and try out different environments until you discover the one that meets your needs.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored three of the most popular Linux Desktop Environments: GNOME, KDE and Xfce. We’ve discussed their features and usability, pros and cons, and popular distributions that use them. We’ve also compared them based on resource usage, customizability, user interface and design, compatibility and availability of applications, and performance and speed. Finally, we’ve discussed how to choose the right Desktop Environment based on your system requirements, user needs, and personal preferences.
Personal Recommendations and Tips
Choosing the right Desktop Environment ultimately depends on your individual needs and preferences. However, based on our comparison of GNOME, KDE and Xfce, we can make some general recommendations.
If you have a modern system with plenty of resources and prefer a modern and streamlined interface, GNOME may be the best choice for you. If you prefer a more traditional interface with lots of customization options and don’t mind sacrificing some performance, KDE may be a better fit. If you prioritize speed and performance, and have an older or low-end system, Xfce may be the way to go.
It’s also important to remember that, based on your requirements, you may always install different Desktop Environments and move between them. If you need to use your system for several reasons or if you have multiple users with varying preferences, this can be quite helpful (e.g. work vs. entertainment).
Final Thoughts on GNOME, KDE and Xfce
Each of the three Desktop Environments has its advantages and disadvantages, and there is no universal solution. GNOME is distinguished for its contemporary and user-friendly interface, but it may place a heavy demand on some systems. KDE is extremely customizable and packed with features, but it may prove overly intricate for certain users. Xfce is swift and lightweight, but it may lack some of the features and finesse that GNOME and KDE offer.
Ultimately, the best Desktop Environment is the one that works best for you. We hope that this article has provided you with the information you need to make an informed decision, and that you enjoy using your Linux Desktop Environment of choice!




