
Top Linux Distros for Math Enthusiasts in 2025
Mathematics is more than just numbers—it’s the language of the universe, the foundation of science, and the key to solving complex problems. Whether you’re a student tackling calculus, a researcher running complex simulations, or a professional working with cryptographic algorithms, having the right tools at your fingertips is crucial. Linux, with its open-source flexibility and powerful computational capabilities, offers some of the best environments for mathematical work. But with so many distributions available, which one should you choose?
In this guide, we explore the top Linux distros for math enthusiasts in 2025, carefully curated to enhance your productivity, streamline your workflows, and provide a seamless mathematical computing experience.
1. Debian Science
If you’re a math enthusiast, researcher, or student looking for a Linux distribution tailored to your needs, Debian Science is an excellent choice. Built on the rock-solid foundation of Debian, this specialized variant provides a comprehensive set of tools and libraries for scientific computing, mathematical modeling, and data analysis. In 2025, Debian Science continues to be one of the top picks for those who need a stable and feature-rich platform for mathematics.

Why Choose Debian Science for Mathematics?
Debian Science is not a separate Linux distribution but rather a collection of curated packages available within the Debian repository. These packages include everything from numerical computing tools to symbolic algebra systems, making Debian an ideal OS for anyone working with complex mathematical problems.
Here’s why Debian Science stands out for math lovers:
1. Stability and Reliability
Debian is well-known for its rock-solid stability. If you need a system that won’t crash while running heavy computations, Debian Science is an excellent choice. Since it’s based on the stable branch of Debian, you get long-term support and reliability, crucial for academic and professional work.
2. Pre-installed and Easily Installable Math Tools
Debian Science provides a huge selection of pre-installed and easily accessible mathematical software, including:
- SageMath – A powerful open-source system for algebra, geometry, number theory, cryptography, and numerical computation.
- GNU Octave – A free alternative to MATLAB, great for numerical analysis.
- Maxima – A computer algebra system for symbolic computation.
- R and RStudio – Ideal for statistical computing and data analysis.
- SciPy and NumPy – Python-based libraries for scientific computing.
- SymPy – A symbolic mathematics package for Python.
- Pari/GP – A great tool for number theory calculations.
- GAP – Used for computational discrete algebra, especially in group theory.
3. Extensive Library Support for Programming
For those who work with programming languages in mathematical research, Debian Science offers extensive support for:
- Python (with SciPy, NumPy, Matplotlib, and SymPy)
- Fortran (GFortran compiler and numerical libraries)
- C/C++ (GCC, Boost, and numerical computation libraries)
- Haskell (for functional programming enthusiasts in mathematics)
4. Open-Source Freedom
One of the biggest advantages of Debian Science is its commitment to free and open-source software. Unlike proprietary tools, you can modify and extend your software stack as needed, making it a perfect choice for academics and professionals who prefer transparency and customization.
5. Easy Package Management with APT
Managing software packages in Debian Science is simple with APT (Advanced Package Tool). You can install any mathematical tool with a single command, such as:
sudo apt install sagemath
sudo apt install octave
sudo apt install maxima
This ease of use makes Debian Science a great choice for those who want a hassle-free Linux experience.
Installing Debian Science
Installing Debian Science is straightforward. You can start with a standard Debian installation and then install the science-mathematics metapackage, which includes all essential math tools:
sudo apt install science-mathematics
Alternatively, you can download and install Debian directly from the official site and select the Science task during installation.
Who Should Use Debian Science?
Debian Science is perfect for:
- Students looking for an affordable and powerful platform for learning mathematics.
- Researchers who need advanced mathematical tools for their work.
- Teachers who want an open-source alternative for educational purposes.
- Data scientists and statisticians who work with large datasets and computational models.
In 2025, Debian Science continues to be a top choice for math enthusiasts who want a stable, powerful, and open-source Linux distribution. With its extensive library of mathematical tools, excellent package management, and strong community support, it’s an ideal platform for anyone serious about mathematics and scientific computing.
If you haven’t tried Debian Science yet, now is the perfect time to explore it and see how it can enhance your mathematical workflow!
2. Fedora Scientific Lab 41
If you’re passionate about mathematics, scientific computing, or data analysis, you need an operating system that is built for the job. Fedora Scientific Lab 41 is one of the best Linux distributions available for math enthusiasts in 2025. With a robust selection of pre-installed mathematical and scientific tools, seamless compatibility with modern hardware, and the reliability of Fedora, this distro is a must-have for researchers, engineers, students, and anyone who loves working with numbers.
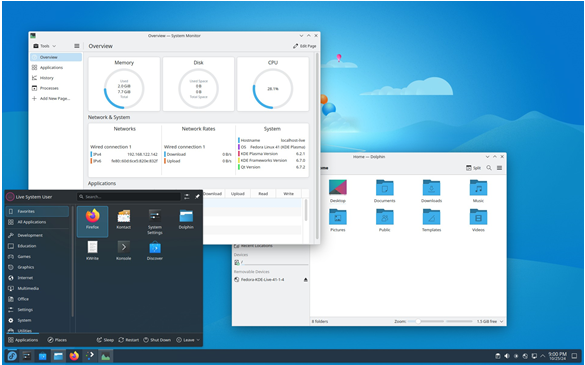
What is Fedora Scientific Lab 41?
Fedora Scientific Lab 41 is a special edition (or “spin”) of Fedora 41, designed specifically for scientists, mathematicians, and engineers. It includes a carefully curated selection of software aimed at numerical computing, symbolic mathematics, statistical analysis, and visualization. The goal is to provide users with an out-of-the-box Linux experience tailored for scientific work without the hassle of manually installing and configuring tools.
Why Choose Fedora Scientific Lab 41?
Fedora Scientific Lab 41 is an excellent choice for math and science enthusiasts due to its:
- Pre-installed Math and Science Software – Skip the tedious installation process and dive straight into problem-solving with industry-standard tools.
- Cutting-Edge Fedora Base – Enjoy the latest updates, security patches, and performance enhancements from Fedora 41.
- Reliability and Stability – Fedora is known for its balance between bleeding-edge features and stability, making it a great choice for serious computational work.
- Open-Source Philosophy – Everything included in Fedora Scientific Lab 41 is free and open-source, ensuring transparency and customizability.
Key Features for Mathematicians
- 1. Comprehensive Math Software Suite
Fedora Scientific Lab 41 comes loaded with essential mathematical tools, including:
- GNU Octave – A powerful open-source alternative to MATLAB for numerical computations.
- SageMath – A robust system for algebra, calculus, number theory, and more.
- Maxima – A symbolic computation engine for solving complex algebraic problems.
- Scilab – Another great numerical computing tool for modeling and simulation.
- SymPy – A Python library for symbolic mathematics, perfect for integration into scripts and research projects.
2. Support for Statistical Computing
For those working with data analysis and statistical modeling, Fedora Scientific Lab 41 includes:
- R and RStudio – The most widely used software for statistical computing and graphics.
- Jupyter Notebook – A flexible environment for interactive computing, supporting Python, R, Julia, and more.
- NumPy, SciPy, and Pandas – The backbone of numerical and data analysis in Python.
- MATLAB-like Alternatives – With tools like GNU Octave and Scilab, users can perform complex computations without needing proprietary software.
3. Advanced Visualization Tools
Understanding complex mathematical data requires excellent visualization tools, and Fedora Scientific Lab 41 delivers with:
- Matplotlib and Seaborn – Python libraries for creating high-quality plots and graphs.
- ParaView – An advanced tool for 3D scientific data visualization.
- Gnuplot – A simple yet powerful tool for plotting mathematical functions and data.
4. LaTeX Support for Mathematical Documentation
Mathematicians and researchers rely on LaTeX for writing papers, research reports, and documentation. Fedora Scientific Lab 41 comes pre-installed with:
- TeX Live – A comprehensive LaTeX distribution.
- Overleaf Integration – Cloud-based collaboration for LaTeX documents.
- Gummi and Texmaker – User-friendly LaTeX editors to streamline document creation.
5. Programming and Scripting Tools
Whether you’re developing mathematical models, scripting calculations, or working with simulations, Fedora Scientific Lab 41 has everything you need:
- Python (with NumPy, SciPy, and SymPy) – Essential for mathematical and scientific programming.
- C, C++, and Fortran Compilers – Ideal for high-performance mathematical computations.
- Julia – A fast and expressive language built for scientific computing.
- GDB and Valgrind – Debugging and performance analysis tools for optimizing code.
Performance and Usability
Fedora Scientific Lab 41 is designed to run efficiently on modern hardware while maintaining a smooth and intuitive user experience. With the GNOME desktop environment as the default, users benefit from a clean interface, excellent performance, and easy navigation. Advanced users can also opt for alternative desktop environments like KDE Plasma or XFCE, depending on their preference.
Fedora’s DNF package manager ensures quick and easy software installation, updates, and dependency management. Additionally, the system supports Flatpak and Snap packages, providing access to a wide range of software beyond the default repositories.
Who Should Use Fedora Scientific Lab 41?
Fedora Scientific Lab 41 is perfect for:
- University students and researchers working on mathematical or scientific projects.
- Data scientists and statisticians analyzing large datasets.
- Engineers and physicists who require advanced computational tools.
- Hobbyists and math enthusiasts exploring numerical computing, algebra, and simulations.
Is Fedora Scientific Lab 41 Worth It?
For anyone deeply involved in mathematics, scientific computing, or data analysis, Fedora Scientific Lab 41 is an excellent choice in 2025. With its vast array of pre-installed tools, a strong Fedora base, and a focus on open-source software, it provides a seamless and powerful environment for all kinds of mathematical work. Whether you’re solving equations, analyzing data, or writing research papers, this distro has you covered.
So if you’re ready to dive into the world of mathematical computing with a Linux distro designed for the job, give Fedora Scientific Lab 41 a try. It might just become your go-to system for all things math and science!
3. Arch Linux (with a Custom Math Setup)
Arch Linux has long been a favorite among power users who enjoy complete control over their system. If you’re a math enthusiast—whether you’re a student, researcher, or just someone who loves tinkering with numbers—setting up Arch Linux with a custom math environment in 2025 is easier and more rewarding than ever.
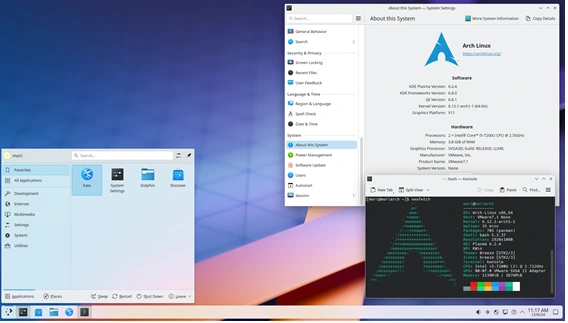
Why Arch Linux for Math Enthusiasts?
Unlike specialized distros like Debian Science or Fedora Scientific, Arch Linux doesn’t come with preinstalled math tools. But that’s actually a good thing! With Arch, you get the flexibility to build your own perfect setup, installing only the tools you need without any unnecessary bloat.
Some key reasons why Arch is great for math users:
- Rolling release model ensures you always have the latest updates.
- AUR (Arch User Repository) gives access to cutting-edge math software.
- Pacman package manager makes installing and updating tools seamless.
- Minimalistic approach means you don’t have to deal with unwanted software.
Getting Started: Installing Arch Linux
If you’re new to Arch, the installation process might seem daunting at first, but it’s well worth the effort. The Arch Wiki provides a step-by-step guide, and tools like archinstall (available in the official ISO) can help automate the setup.
Once you have a base system running, it’s time to build your ideal math environment.
Essential Math Software for Arch Linux
Here’s a breakdown of the best math tools you can install on Arch Linux:
1. Programming and Scripting
- Python + NumPy/SciPy/SymPy – Perfect for numerical and symbolic computation.
sudo pacman -S python-numpy python-scipy python-sympy
- SageMath – An all-in-one open-source math software system.
sudo pacman -S sagemath
- Julia – High-performance computing for numerical analysis.
sudo pacman -S julia
2. Algebra and Symbolic Computation
- Maxima – Computer algebra system for symbolic computation.
sudo pacman -S maxima wxmaxima
- Mathematica (optional, proprietary) – If you have a license, you can install it manually.
3. Statistics and Data Analysis
- R and RStudio – Great for statistical computing and visualization.
sudo pacman -S r rstudio-desktop
4. Graphing and Visualization
- Gnuplot – A lightweight plotting tool.
sudo pacman -S gnuplot
- Matplotlib (Python) – A powerful library for creating plots.
sudo pacman -S python-matplotlib
5. LaTeX for Math Documentation
For writing math-heavy documents, LaTeX is a must:
sudo pacman -S texlive-most texlive-lang
Optimizing Your Math Setup
1. Use a Tiling Window Manager
If you want a distraction-free workspace, consider using i3 or bspwm for better workflow management.
sudo pacman -S i3
2. Enable GPU Acceleration for Faster Computations
Many math programs benefit from GPU acceleration. If you have an NVIDIA GPU, install CUDA:
sudo pacman -S cuda cudnn
3. Keep Everything Updated
Since Arch is a rolling release distro, staying up-to-date is crucial. Run:
sudo pacman -Syu
Arch Linux with a custom math setup is one of the most powerful environments for math enthusiasts in 2025. While it requires some initial effort to set up, the flexibility and control you gain are unmatched. Whether you’re solving complex equations, working on research, or just exploring the world of mathematics, Arch lets you build exactly what you need. Would you like to see a pre-configured Arch Linux math setup with an easy installer in the future? Let me know in the comments! 🚀
4. Kali Linux (For Cryptographers & Security Mathematicians)
When it comes to cybersecurity, cryptography, and mathematical security analysis, Kali Linux stands out as a powerhouse. Designed primarily for penetration testing and security auditing, it offers a vast arsenal of tools that cater not just to ethical hackers but also to cryptographers and security mathematicians. If you are passionate about cryptographic algorithms, mathematical proofs, or secure computing, Kali Linux provides a solid foundation to build upon.
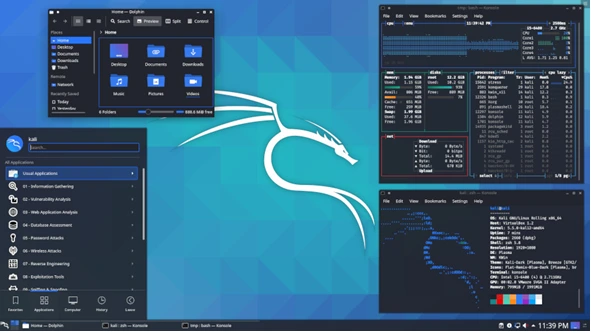
Why Kali Linux for Cryptography & Security Mathematics?
1. Built for Security Research & Mathematical Analysis
Unlike general-purpose Linux distributions, Kali Linux is designed for security professionals. This makes it an ideal platform for cryptographers and mathematicians who specialize in encryption, decryption, and cryptanalysis. The system is optimized for penetration testing, reverse engineering, and forensic analysis, all of which heavily rely on mathematics.
2. Preloaded with Cryptography & Security Tools
Kali Linux comes packed with cryptographic tools that help develop, test, and break encryption schemes. Whether you’re working with RSA, ECC, AES, or quantum-resistant cryptography, Kali has something for you.
3. Support for Advanced Mathematical Libraries
Kali Linux supports powerful math-centric programming languages such as:
- Python (with NumPy, SymPy, SciPy) – Ideal for mathematical modeling and cryptographic simulations.
- SageMath – A powerful open-source tool for advanced algebra, number theory, and cryptographic computations.
- MATLAB Alternatives (GNU Octave, Scilab) – Useful for matrix algebra and algorithm prototyping.
Essential Cryptography & Security Tools in Kali Linux
1. Hashcat (Password & Hash Cracking)
For cryptographers studying hash functions, Hashcat is a must-have. It supports MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, and even bcrypt. Security mathematicians often use it for hash function analysis and collision resistance testing.
2. John the Ripper (Brute-force Analysis)
This classic password cracker helps test cryptographic strengths and analyze the mathematical efficiency of hash algorithms.
3. OpenSSL (Encryption & Decryption)
A widely used cryptographic library, OpenSSL allows you to:
- Generate and verify RSA and ECC keys
- Encrypt and decrypt AES-based messages
- Perform TLS/SSL security analysis
4. GnuPG (PGP Encryption)
If you’re interested in public-key cryptography, GnuPG lets you generate secure key pairs, encrypt files, and sign messages using GPG/PGP standards.
5. Cryptool (Visual Cryptography & Learning)
A great tool for teaching cryptographic concepts. It offers a GUI-based approach for exploring:
- Prime number factorization
- RSA key generation
- Cryptanalysis of classic ciphers
6. RsaCtfTool (RSA Algorithm Analysis)
For security mathematicians interested in breaking weak RSA implementations, RsaCtfTool helps in factorizing keys, testing padding schemes, and analyzing vulnerabilities.
7. Wireshark (Packet Analysis & Encryption Inspection)
Cryptographers studying network security and encrypted traffic use Wireshark to:
- Capture TLS/SSL-encrypted packets
- Analyze Diffie-Hellman key exchanges
- Study AES-encrypted communications
Setting Up Kali Linux for Cryptographic Research
1. Install Essential Math Libraries
Run the following commands to install crucial mathematical tools:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install sage python3-sympy python3-numpy gnuplot
2. Configure a Secure Development Environment
- Use Jupyter Notebook for cryptographic research:
sudo apt install jupyter-notebook
jupyter-notebook
- Enable full-disk encryption (LUKS) for protecting sensitive research data.
3. Set Up a Quantum-Safe Cryptography Sandbox
If you’re experimenting with post-quantum cryptography, install OpenQuantumSafe (OQS) for researching lattice-based encryption:
git clone https://github.com/open-quantum-safe/liboqs.git
cd liboqs
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make -j$(nproc)
sudo make install
Kali Linux vs Other Linux Distros for Math & Security
| Feature | Kali Linux | Fedora Scientific | Debian Science | Arch Linux (Custom Math Setup) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptography Tools | ✅ Pre-installed | ❌ Limited | ❌ Limited | ❌ Requires setup |
| Penetration Testing | ✅ Built-in | ❌ Not included | ❌ Not included | ❌ Not included |
| Security Focus | ✅ High | 🔹 Science-focused | 🔹 Science-focused | 🔹 Highly customizable |
| Mathematics Support | ✅ Strong (via SageMath, Python, OpenSSL) | ✅ Strong | ✅ Strong | ✅ Customizable |
While Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, and Arch offer good math tools, only Kali Linux provides a ready-to-use cryptographic and security-focused environment.
Why Choose Kali Linux for Math & Security?
Kali Linux is more than just a penetration testing distro—it’s a powerful platform for cryptographers and security mathematicians. Whether you’re developing new encryption algorithms, testing cryptographic weaknesses, or analyzing cybersecurity threats mathematically, Kali offers the best set of tools out-of-the-box.
If you’re passionate about mathematical security research, cryptographic modeling, or network encryption, Kali Linux in 2025 is the best Linux distribution for your work.
Are you ready to take your cryptographic research to the next level? Give Kali Linux a try today!
5. Gentoo Linux (For Power Users in Mathematics)
When it comes to Linux distributions, most users fall into two categories: those who want a simple, plug-and-play experience and those who love to customize every detail of their system. If you’re in the second group, especially if you’re a math enthusiast, then Gentoo Linux is a perfect match.
Gentoo isn’t just another Linux distro—it’s a power user’s paradise. It gives you complete control over your system, allowing you to compile software from source, optimize performance, and fine-tune every aspect of your computing experience. If you’re doing high-level mathematical computing, cryptography, or research-heavy work, this level of control can be a game changer.

Why Math Enthusiasts Should Consider Gentoo
1. Ultimate Performance for Heavy Calculations
Mathematical computing often involves complex simulations, numerical analysis, and symbolic computations. With Gentoo, you can compile everything for your exact CPU architecture, squeezing out every bit of performance from your system. Whether you’re running MATLAB, SageMath, GNU Octave, or TensorFlow, the extra speed matters.
2. Fine-Tuned Package Management with Portage
Unlike traditional package managers like APT (Debian/Ubuntu) or DNF (Fedora), Gentoo’s Portage is built around the concept of compiling software from source. This means you can enable only the features you need, reducing bloat and ensuring that your math tools run optimally.
For example, when installing SciPy, you can compile it specifically with Intel MKL or OpenBLAS support, which can significantly boost performance for linear algebra operations.
3. Custom Kernel Optimization for Math Workloads
Mathematicians and researchers often work with high-performance computing (HPC), and Gentoo allows you to customize the Linux kernel to prioritize mathematical workloads. You can strip out unnecessary modules, optimize for real-time processing, and even apply patches for specific CPU architectures like AMD Zen or Intel Xeon.
4. Support for LaTeX, Symbolic Computation, and Cryptography
Mathematicians frequently use LaTeX for writing research papers, SageMath for symbolic computation, and GAP for discrete algebra. Gentoo’s flexibility lets you install and configure these tools exactly the way you want.
For cryptographers, Gentoo also supports GMP, OpenSSL, and NTL, allowing fine-grained control over cryptographic libraries and algorithms—ideal for research in number theory and security mathematics.
Getting Started with Gentoo for Mathematics
1. Install a Minimal Base System
Unlike Ubuntu or Fedora, Gentoo doesn’t come with a pre-configured setup. You’ll need to install a base system, configure your USE flags (which dictate software features), and compile everything from scratch. This might sound daunting, but it ensures that every part of your system is tailored to your needs.
2. Choose the Right Compiler and Optimizations
Most math software benefits from optimized compiler flags. Using GCC with aggressive optimization settings like -march=native -O3 can improve performance in numerical computations.
3. Set Up a Math-Friendly Environment
Here’s a quick list of must-have packages for mathematics on Gentoo:
- SciPy & NumPy – Essential for numerical computing
- SageMath – A powerful open-source alternative to Mathematica
- GAP – For discrete algebra and computational group theory
- Maxima – A computer algebra system for symbolic computation
- LaTeX (TeX Live) – For writing research papers
- GMP & MPFR – High-precision arithmetic libraries
You can install these using Portage:
emerge –ask sci-libs/scipy sci-mathematics/sagemath dev-libs/gmp app-text/texlive
Who Should Use Gentoo for Math?
Gentoo is not for the faint of heart. If you prefer a system that “just works” out of the box, something like Ubuntu Mathematics Remix or Debian Science might be a better fit.
However, if you’re a power user, researcher, or someone who loves fine-tuning your system for maximum efficiency, then Gentoo is worth the investment. It’s a distro that rewards patience and expertise with unmatched speed, flexibility, and control.
Gentoo Linux isn’t just an operating system—it’s a lifestyle. If you love math and computing, the ability to build a fully optimized environment tailored to your exact needs is empowering. Yes, the learning curve is steep, but the payoff is incredible.
So, if you’re a math enthusiast who wants total control over your computing environment, Gentoo is calling your name.
Final Thoughts
When it comes to mathematics-focused Linux distributions, your choice should align with your needs and expertise level. Gentoo Linux is the go-to option for power users who demand maximum performance and control over their computational environment. If you are into cryptography and security-related mathematics, Kali Linux offers specialized tools for encryption and cybersecurity analysis. Arch Linux, with a custom setup, is ideal for those who prefer a minimalist and optimized workflow tailored to their mathematical requirements. Fedora Scientific Lab 41 provides a ready-made environment with cutting-edge mathematical tools, making it a great choice for data scientists and researchers. Finally, Debian Science is the epitome of stability, offering a solid foundation for academic research and long-term mathematical projects.
Regardless of which distro you choose, Linux offers a rich ecosystem for mathematical exploration, computational efficiency, and research-driven workflows. Pick the one that best suits your mathematical journey and dive into the world of limitless possibilities. Happy computing!
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. While we strive to ensure accuracy, Linux distributions are frequently updated, and features may change over time. Users should conduct their own research and testing to determine which Linux distribution best fits their specific needs. We are not affiliated with any of the distributions mentioned and do not guarantee the performance or security of any particular system. Use at your own discretion.
Also Read
Top 5 Linux Distributions for Students in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide




