
Linux for TV Customizing Your Home Entertainment System
Tired of being boxed in by the limitations of your smart TV? Imagine transforming your television into a powerhouse of entertainment that’s fully customizable, secure, and perfectly aligned with your preferences. Enter Linux—a versatile, open-source operating system that’s revolutionizing home entertainment for tech enthusiasts and casual users alike. Whether you crave greater control over your media, want to breathe new life into older hardware, or simply value your digital privacy, Linux offers endless possibilities to craft the ultimate viewing experience.
Ready to cut the cords of restriction and dive into a world of limitless entertainment? Let’s explore how Linux can turn your TV into a personalized entertainment hub.
Why Choose Linux for TV?
Linux is known for its flexibility, stability, and wide range of distributions (distros) tailored to different use cases. Using Linux on your TV or as part of your home entertainment system offers several advantages:
- Freedom and Control: With Linux, you are not bound by the limitations of proprietary smart TV operating systems. You can install, modify, and configure software as per your needs.
- Cost-Effective: Linux is free to use, making it an excellent choice for budget-conscious users who want to maximize their home entertainment without spending on expensive software or devices.
- Performance: Lightweight Linux distributions (distros) can breathe new life into older hardware, ensuring smooth performance even on less powerful devices.
- Privacy: Unlike many smart TV OSs that track your viewing habits, Linux respects your privacy.
Choosing the Right Linux Distribution for TV
Not all Linux distros are suitable for TV use. Here are some of the best options:
1: Kodi (LibreELEC or OSMC):
Kodi has revolutionized home entertainment, transforming devices into powerful media centers. When it comes to setting up Kodi on a Linux-based system for your TV, LibreELEC and OSMC stand out as the leading distributions. Each offers unique benefits, and selecting the right one depends on your needs and technical proficiency. This guide will help you decide which is best for your setup.
Understanding Kodi, LibreELEC, and OSMC
Kodi is an open-source media player that organizes and plays various media formats. It’s highly customizable with add-ons and skins, making it ideal for a personalized media experience.
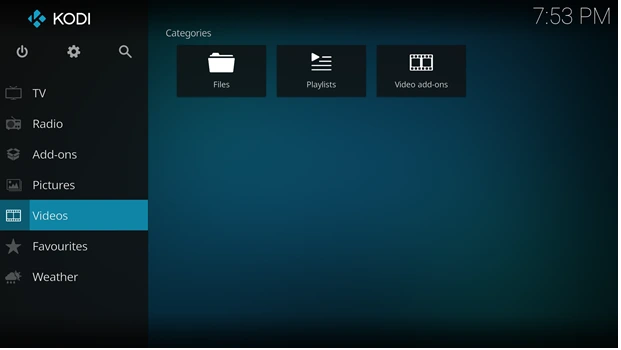
LibreELEC (Libre Embedded Linux Entertainment Center) is a lightweight, Just Enough OS (JeOS) designed solely to run Kodi. It emphasizes speed, simplicity, and minimal system resource use.
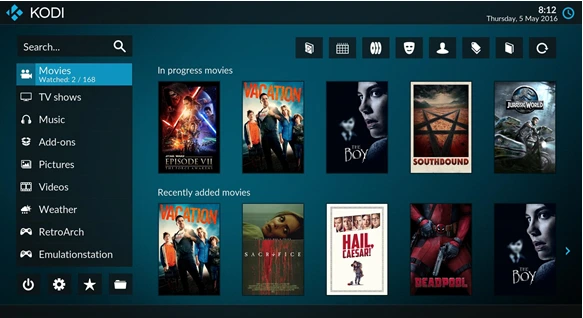
OSMC (Open Source Media Center) is a full Linux-based media center operating system built around Kodi. It offers greater flexibility and access to the underlying Linux system, allowing for additional software installations and custom configurations.

LibreELEC: Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Lightweight and Fast: Designed exclusively for Kodi, LibreELEC is optimized for performance and quick boot times.
- Ease of Use: Its minimal interface makes it ideal for users who want a plug-and-play experience.
- Stable and Reliable: Focuses on delivering a consistent and stable Kodi experience.
- Automatic Updates: Simplified update system keeps Kodi and LibreELEC up-to-date.
Cons:
- Limited Flexibility: Restricted to Kodi-centric functions; not suitable for other Linux applications.
- Minimal Customization: Advanced customizations are limited compared to a full Linux OS.
OSMC: Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Full Linux OS: Allows installation of additional software beyond Kodi.
- User-Friendly Interface: Polished and modern UI, with easy navigation and settings management.
- Customizability: Offers more opportunities for advanced users to tweak and enhance their setup.
- Broad Hardware Support: Compatible with various devices like Raspberry Pi, Vero, and older Apple TVs.
Cons:
- Heavier Resource Use: Slightly more demanding than LibreELEC, which can affect performance on low-end devices.
- Longer Setup Time: Requires more configuration, making it less ideal for beginners seeking a quick setup.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choose LibreELEC if:
- You want a simple, hassle-free media center.
- You’re using a low-powered device (e.g., Raspberry Pi, low-end Android TV boxes).
- Speed and stability are your top priorities.
Choose OSMC if:
- You want to run additional applications alongside Kodi.
- You prefer more control over your system.
- You’re comfortable with Linux or want to explore more customization options.
LibreELEC and OSMC both deliver excellent Kodi experiences but cater to different audiences. LibreELEC shines for those seeking simplicity and speed, while OSMC appeals to users looking for flexibility and expanded functionality. By understanding their strengths and limitations, you can choose the distribution that best aligns with your home entertainment needs.
Whichever you choose, Kodi’s vast capabilities will turn your TV into a dynamic media hub.
2: Ubuntu TV:
In the evolving landscape of smart TVs and home entertainment, Linux distributions have carved out a significant niche by offering customizable and efficient solutions. Among these, Ubuntu TV stands out as a compelling choice for those seeking a robust and user-friendly TV operating system. This blog post explores why Ubuntu TV could be the ideal Linux distribution for your television setup and how it compares to other alternatives.
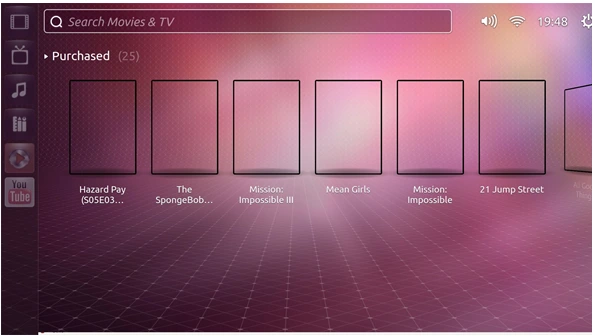
What is Ubuntu TV?
Ubuntu TV is an adaptation of the popular Ubuntu Linux distribution designed specifically for television interfaces. It blends Ubuntu’s reliability and security with an intuitive user interface optimized for larger screens and remote navigation. Aimed at delivering a seamless multimedia experience, Ubuntu TV offers features like media streaming, live TV, and integration with online content services.
Why Choose Ubuntu TV?
1. User-Friendly Interface:
Ubuntu TV is designed with simplicity in mind, making it easy for users of all technical levels to navigate through apps, settings, and multimedia content.
2. Customizability:
As an open-source platform, Ubuntu TV allows users to tailor their system to personal preferences, from the user interface to the types of apps installed.
3. Strong Community Support:
Backed by the extensive Ubuntu community, users can access a wealth of resources, forums, and tutorials to troubleshoot issues and expand functionality.
4. Security and Stability:
Built on Ubuntu’s solid foundation, Ubuntu TV benefits from regular security updates and a stable operating environment, crucial for a reliable home media setup.
Comparing Ubuntu TV to Other Linux Distributions for TV
Other Linux distributions like Kodi (via LibreELEC), OpenELEC, and Android TV (Linux-based) also offer robust media center capabilities. However, Ubuntu TV distinguishes itself with its combination of user-friendliness, security, and the ability to run a wider range of Linux applications. While Kodi excels in media playback customization, Ubuntu TV provides a more holistic operating system experience suitable for various tasks beyond media consumption.
Is Ubuntu TV Right for You?
Ubuntu TV is ideal for users who value a secure, customizable, and user-friendly smart TV experience. It’s particularly well-suited for tech enthusiasts and DIY users who enjoy tweaking their systems. However, those looking for a plug-and-play solution with minimal setup might prefer alternatives like Android TV or Roku.
Getting Started with Ubuntu TV
To install Ubuntu TV, you’ll need compatible hardware and a bit of technical know-how. Installation guides and community forums provide step-by-step instructions to help you set up and optimize your system. Once installed, you can explore various apps, streaming services, and even integrate smart home functionalities.
Choosing the right Linux distribution for your TV setup depends on your specific needs and technical comfort level. Ubuntu TV offers a compelling blend of user-friendliness, security, and flexibility, making it a standout choice for many users. Whether you’re transforming your TV into a multimedia powerhouse or seeking a more open and customizable smart TV experience, Ubuntu TV is well worth considering.
3: Plex Media Server (on any Linux Distro):
Plex Media Server is a powerhouse for organizing and streaming your media collection across multiple devices. While Plex runs on various operating systems, Linux stands out for its performance, flexibility, and low resource consumption. However, with so many Linux distributions available, choosing the right one can be tricky. Let’s explore the best Linux distros for running Plex Media Server and what makes them ideal for your entertainment hub.
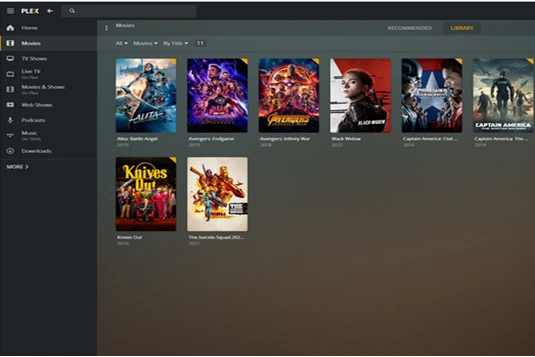
1. Ubuntu Server
Why It’s Great: Ubuntu Server is one of the most popular Linux distributions, known for its stability and large community support. It offers long-term support (LTS) releases, making it a solid choice for a server that needs to run reliably over time. Installation is straightforward, and most Plex installation guides cater to Ubuntu users.
Best For: Beginners and users who want a hassle-free setup.
2. Debian
Why It’s Great: Debian is the parent distribution of Ubuntu, known for its stability and performance. It’s slightly more minimal than Ubuntu, which can lead to better resource management. Debian’s conservative approach to software updates ensures a stable and secure media server.
Best For: Users who value stability over bleeding-edge features.
3. Fedora Server
Why It’s Great: Fedora is known for being cutting-edge, providing the latest features and software updates. Fedora Server is optimized for server use and comes with modern tools and technologies that can enhance Plex’s performance.
Best For: Users who like staying updated with the latest Linux technologies.
4. Arch Linux
Why It’s Great: Arch Linux is all about customization and control. If you want to build a lightweight, streamlined server, Arch lets you install only what you need. The Arch Wiki is a comprehensive resource for troubleshooting and configuration.
Best For: Advanced users who want complete control over their setup.
5. openSUSE Leap
Why It’s Great: openSUSE Leap offers a balance between stability and modern features. With tools like YaST for system administration, managing your server becomes more intuitive.
Best For: Intermediate users seeking a balance between stability and customization.
6. Linux Mint
Why It’s Great: While Linux Mint is primarily desktop-oriented, it’s built on Ubuntu, making it compatible with most Plex guides. Mint’s user-friendly interface can be a plus if you plan to manage the server directly.
Best For: Users transitioning from Windows or those who prefer a GUI.
Key Factors to Consider
- Ease of Use: If you’re new to Linux, opt for user-friendly distributions like Ubuntu or Linux Mint.
- Stability: For uninterrupted streaming, Debian or Ubuntu LTS versions are ideal.
- Resource Efficiency: Lightweight distributions like Arch or Debian can maximize performance on older or low-power hardware.
- Community Support: Distributions with large communities, like Ubuntu and Fedora, offer more tutorials and troubleshooting help.
The best Linux distribution for Plex Media Server depends on your comfort level with Linux and your hardware capabilities. For most users, Ubuntu Server offers the best balance of ease and performance. Advanced users might prefer Arch Linux for customization, while Debian provides rock-solid stability. No matter which distribution you choose, Linux ensures your Plex Media Server runs smoothly and efficiently, giving you uninterrupted access to your media library.
Happy streaming!
4: Android TV via Linux Kernel:
In the world of smart TVs, Android TV has carved a niche for itself by providing a rich multimedia experience powered by the Linux kernel. For developers and enthusiasts looking to create or optimize Android TV devices, selecting the right Linux distribution is a critical step. The choice influences system performance, hardware compatibility, and development flexibility. Let’s dive into how to choose the right Linux distribution for Android TV development.
Understanding the Role of the Linux Kernel in Android TV
Android TV operates on top of the Linux kernel, which serves as the foundation for hardware interaction, resource management, and security. However, Android isn’t a traditional Linux distribution. It uses a customized kernel and user-space tools designed specifically for mobile and embedded devices. Therefore, the underlying Linux distribution must support these specialized requirements.
Key Factors in Choosing a Linux Distribution
1: Hardware Compatibility
Different distributions offer varying levels of hardware support. For Android TV, the chosen distribution should support ARM-based processors, GPUs, and multimedia hardware acceleration. Popular distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, and Yocto offer broad compatibility and modularity for embedded systems.
2: Performance Optimization
A lightweight and optimized distribution ensures smoother performance on resource-constrained TV hardware. Distributions like Alpine Linux and Buildroot are designed to be minimalistic and can be fine-tuned for specific use cases.
3: Security and Stability
Security is paramount for smart devices connected to the internet. Distributions with strong security practices, regular updates, and a large support community (such as Ubuntu Core) are excellent choices. Long-Term Support (LTS) versions provide stability over extended periods.
4: Development Ecosystem
A robust development ecosystem with tools, documentation, and community support accelerates development. Yocto Project, for example, allows for creating custom Linux distributions tailored to specific hardware and software needs.
5: Update and Maintenance
SupportSmart TVs require regular updates to address security vulnerabilities and performance improvements. Choosing a distribution that supports over-the-air (OTA) updates, like Ubuntu Core, ensures devices remain secure and efficient.
Top Linux Distributions for Android TV Development
1: Yocto Project
Yocto is highly customizable, making it ideal for creating a tailored Linux environment for Android TV. It supports various hardware platforms and allows fine-grained control over system components.
2: Ubuntu Core
A streamlined version of Ubuntu, designed for IoT and embedded devices. It offers robust security, OTA updates, and a strong support ecosystem, making it suitable for smart TVs.
3: Buildroot
Known for its simplicity and lightweight footprint, Buildroot is perfect for creating minimal Linux systems. It is ideal for resource-limited devices like smart TVs.
4: Debian
Debian’s stability and extensive package repository make it a solid choice for development, especially if customization and community support are priorities.
Selecting the right Linux distribution for Android TV development hinges on balancing hardware compatibility, performance, security, and ease of development. Yocto offers unmatched customization, Ubuntu Core provides security and ease of maintenance, and Buildroot excels in lightweight performance. By carefully evaluating these factors, developers can craft a seamless and secure Android TV experience that stands out in the competitive smart TV market.
Setting Up Linux on Your TV
1: Hardware Requirements:
- A compatible PC, Raspberry Pi, or similar device to connect to your TV.
- An HDMI cable for video output.
- Optional: A wireless keyboard, mouse, or remote control for easier navigation.
2: Installation Steps:
- Download a Linux Distro: Choose a distro like LibreELEC, OSMC, or any lightweight Linux OS. Download the ISO file from the official website.
- Create Bootable Media: Use tools like Balena Etcher or Rufus to create a bootable USB drive.
- Install Linux on Your Device: Boot your device from the USB drive and follow the installation prompts. Customize the setup as needed.
3: Configuration:
- Drivers and Updates: Ensure all necessary drivers (e.g., GPU drivers) are installed for optimal performance.
- Media Center Software: Install Kodi, Plex, or any preferred media center application.
- Network Setup: Configure Wi-Fi or Ethernet for streaming and remote access.
Customizing Your Home Entertainment System
1: Media Playback:
- Organize your media library with tools like Plex or Kodi. Add metadata, posters, and descriptions for a professional look.
- Enable streaming services such as Netflix, Amazon Prime, or Disney+ using compatible add-ons or web browsers.
2: Gaming:
- Install Steam or retro gaming emulators like RetroArch to turn your Linux-based system into a gaming console.
3: Smart Home Integration:
Use Linux to control smart home devices. Applications like Home Assistant can be installed to manage lighting, security cameras, and more from your TV.
4: Web Browsing and Productivity:
Install web browsers like Firefox or Chromium for casual browsing. Use LibreOffice for productivity tasks on the big screen.
5: Customization:
Change the appearance of your Linux desktop environment to suit your taste. Install themes, icons, and wallpapers for a personalized experience.
Tips for Optimizing Performance
- Choose Lightweight Distros: For devices with limited resources, opt for lightweight distros like Xubuntu or Lubuntu.
- Enable Hardware Acceleration: Ensure your media center software supports GPU acceleration for smoother playback.
- Regular Updates: Keep your Linux system updated for security and performance enhancements.
- Backup Configuration Files: Save a copy of your configuration files in case you need to reinstall or switch distros.
Final Thoughts
Using Linux to power your home entertainment system is a rewarding experience that offers unparalleled flexibility and customization. Whether you’re a movie buff, a gamer, or someone who values privacy, Linux can cater to your specific needs while giving you complete control over your setup. So why settle for off-the-shelf solutions when you can create a bespoke entertainment system that’s truly yours?
Ready to take the plunge? Grab a Linux distro, fire up your hardware, and start building the home entertainment system of your dreams.
Happy customizing and streaming!
Disclaimer
This blog post is intended for informational purposes only. Modifying your TV setup with Linux-based systems may require technical knowledge and can void warranties or impact device functionality. Always ensure compatibility with your hardware and back up important data before proceeding. The author and publisher are not responsible for any damage or data loss resulting from the implementation of suggestions provided in this article. Proceed at your own discretion and risk.
Also Read
Top 5 Linux Distributions for Mac Lovers: Capturing the macOS Essence




